Hunters don’t want a crew of researchers to inform us that making noise within the woods spooks recreation — we’ve identified that for millennia. What we will’t at all times inform is how a lot racket wild critters will tolerate earlier than they run off, or what widespread outside actions strain them most. Now a few of these questions have been answered because of a brand new examine that examined how the noise of accelerating outside recreation is affecting wildlife.
The examine, which was revealed in the July 2024 challenge of Present Biology, examines how recreation reacts when confronted with the vocal and non-vocal sounds of small and enormous teams of hikers, path runners, mountain bikers, and off-road automobile customers. All instructed, wildlife was 4.7 occasions extra more likely to flee from all human noises and people critters remained vigilant thrice longer than when no or pure noise was performed. What’s extra, wildlife abundance on the digicam websites was 1.5 occasions decrease the week after recreation noise was performed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=/rZGAjoaYFTs
Clips of big-game reacting to recreation noises: Black bear flees from the sounds of a small group of hikers; a mule deer is vigilant to, then flees from, mountain biker sounds; an elk runs from OHV noise. You may watch extra path digicam footage right here. Video courtesy of Rocky Mountain Analysis Station
To conduct the examine, researchers with the U.S. Forest Service and several other Western universities deployed path digicam traps and audio system in Wyoming’s Bridger-Teton Nationwide Forest. When triggered the audio system performed pre-recorded sounds of out of doors customers, plus management sounds of non-human exercise and no noise in any respect. They collected and analyzed information from 1,023 audio-trigger occasions throughout 4,444 lure nights of mule deer, elk, purple fox, black bears, moose, pronghorn, cougars, coyotes, and wolves.
The recordings that scared animals probably the most have been giant vocal teams of hikers; animals have been eight occasions as more likely to run off after they heard chatty backpackers and reacted equally to giant teams of vocal bikers. Whereas recreation didn’t flee as usually from the sounds of off-road automobiles, animals remained vigilant the longest after listening to four-wheelers close by in comparison with another consumer group.

Picture courtesy of Rocky Mountain Analysis Station
Out of the animals studied, elk proved probably the most delicate to human recreation sounds and had a virtually 50 p.c chance of fleeing; additionally they stayed vigilant the longest after operating off. Black bears have been the second-most more likely to flee at about 40 p.c chance, adopted by pronghorn at 25 p.c. Moose, mule deer, and coyotes all registered roughly the identical, at under 20 p.c.
“Although moose and mule deer had decrease possibilities of fleeing than elk, black bear, and pronghorn, each have been proven to keep away from areas with human recreation in different research,” the researchers write. “Nevertheless, moose have additionally been proven to pick for areas of human presence, presumably as a human protect impact from predators, indicating risk-reward tradeoffs and that responses to recreation noise could also be state of affairs dependent.”
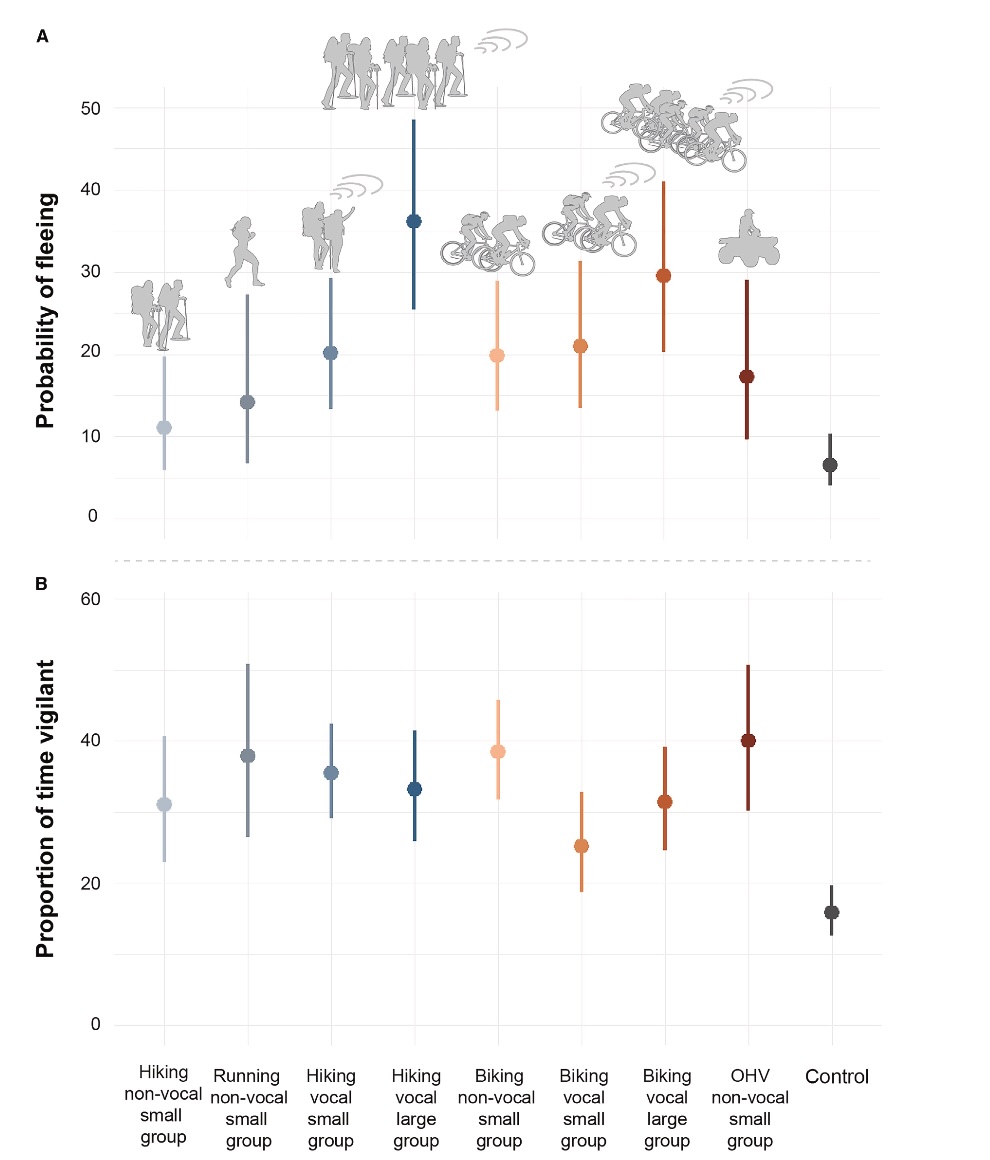
Graphs courtesy of the Rocky Mountain Analysis Station
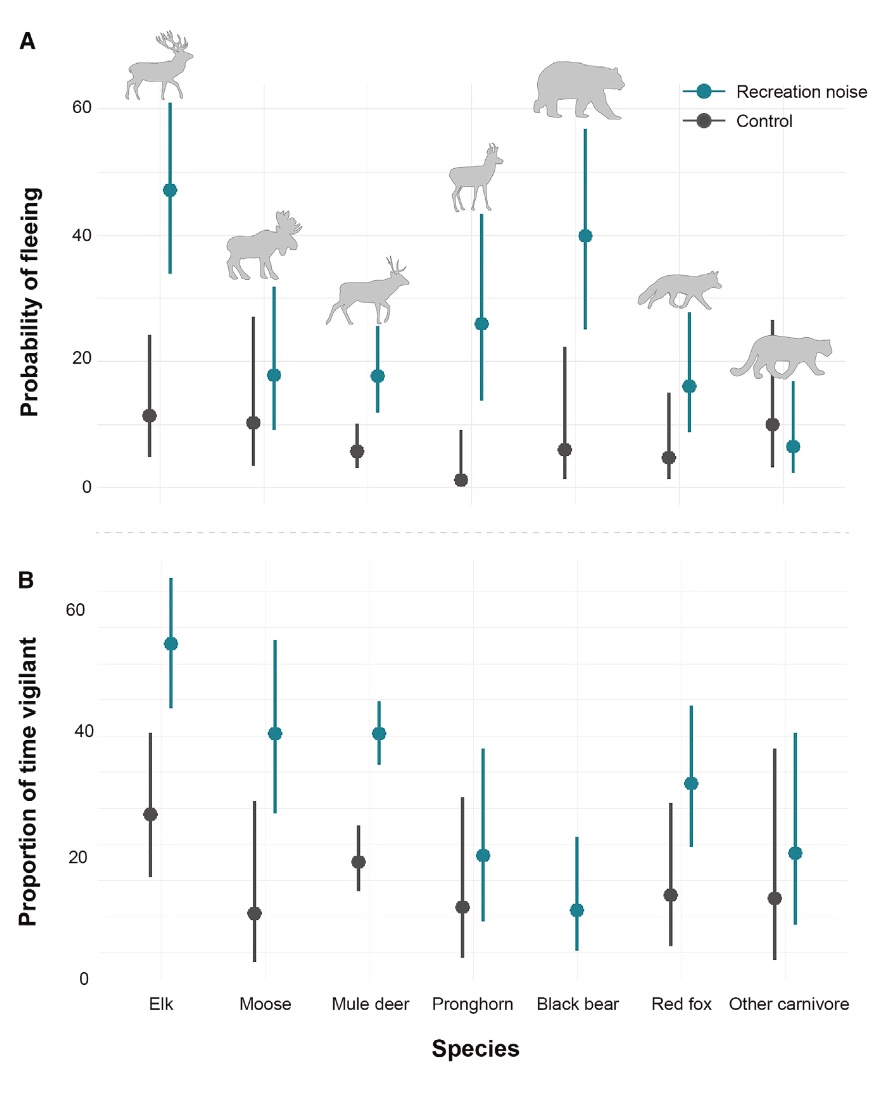
Graphs courtesy of the Rocky Mountain Analysis Station
Massive carnivores proved the least delicate to human noise; cougars didn’t seem to reply otherwise to human recreation sounds than they did to no noise in any respect. Researchers famous, nonetheless, that there have been limitations to conclusions that human recreation noise doesn’t trouble the large cats.
“Although carnivores in our examine had a weak behavioral response to recreation noise, they could nonetheless have been experiencing physiological results that we have been unable to watch. For instance, larger stress hormone ranges have been present in wolves in response to snowmobile recreation, and although few behavioral adjustments have been noticed, acute will increase in coronary heart charges have been documented in black bears in response to unmanned aerial automobiles. Subsequently, lack of an apparent behavioral response might not equate to lack of response, and our outcomes are doubtless underrepresenting the breadth of results of recreation noise.”

Picture courtesy of Rocky Mountain Analysis Station
In fact, the examine didn’t look at elements like human scent or the visible presence of recreation, however it wasn’t imagined to; researchers wished to drill-down particularly into how noise impacts wildlife. The upshot, they are saying, is that even low-levels of recreation noise might trigger wildlife to keep away from prime habitat — and the forage and canopy it affords. All these findings might finally result in completely different (learn: extra restrictive) recreation guidelines.
In grizzly nation the place persons are suggested to journey in bigger teams and make a lot of noise, researchers say recreation managers may take into account altering guidelines to “prohibit recreationists to remain on designated trails.”
Learn Subsequent: Alaska Officers Kill 81 Bears, 14 Wolves to Assist Caribou Calves
Whereas the examine particulars are attention-grabbing, the teachings for hunters who wish to achieve success are acquainted: Hunt solo or in small teams, get away from different individuals, and hold your mouth shut. Oh, and driving your ATV to your deer stand isn’t as stealthy as you may assume.
This story was up to date to incorporate video footage and path digicam photographs from researchers Katherine Zeller and Mark Ditmer.


